Cabbage is a versatile garden crop. Hardy and easy-to-grow, cabbage is the perfect addition to your garden and grows great alongside beans, herbs and other brassicas.
Growing cabbage is very easy, and there are many different varieties you can grow in the garden, from early producers to late-fall crops. Interested in how to grow cabbage? This guide has it all, from cabbage growing stages, to seed starting tips.
Growing Cabbage 101: Step-by-Step Guide

1. Location
Cabbage requires about 6-8 hours of direct sunlight. Plant in full sun.
2. Temperature and Humidity
Cabbage prefers cool and moderate temperatures for optimal growth.
3. Spacing
Plant cabbage about 12-18 inches apart in rows, depending on their variety.
4. Soil
Cabbage prefers fertile and well-draining soil rich in organic matter. The pH level of the soil should be 6 to 7.
5. Nutrients
Use a balanced fertilizer or a fertilizer made for vegetables to supply additional nutrients throughout the growing season.
6. Water
Water plants deeply to maintain the soil moisture. Give 1-2 inches of water per week.
7. Mulch
Apply an organic mulch layer of shredded leaves, straw, or grass clippings, but provide space around the stems.
How to Grow Cabbage from Seeds?
- Select a wide seed tray to sow cabbage seeds.
- Fill it with a seed starting mix or soil enriched with organic matter.
- Fill the seed tray loosely with 2 to 3 layers of potting mix.
- Sprinkle seeds on the soil and cover it with a thin layer of soil.
- After sowing, moisten the soil.
- Cover the seed tray with a mulching sheet to maintain adequate temperature and moisture levels.
- Shift the tray to a location where it receives 2-3 hours of sunlight daily.
- Seeds germinate in 7-15 days.
- Seedlings take 4-6 weeks to get ready for transplantation. The germination period may vary depending on the climate and location.
- When it reaches 3-4 inches in height and has produced 2 to 3 sets of true leaves, cabbage is ready to transplant.
How to Grow Cabbage in Containers?
Start seeds indoors about 4 weeks before the last frost date in spring or 6-8 weeks before the frost date in autumn. Transplant seedlings in containers when the seeds are a month old.
- Choose containers which are 12 inches deep and 18 inches in diameter with proper drainage holes.
- Fill it with garden soil mix and rich organic matter.
- Use organic compost or a slow release balanced 10-10-10 fertilizer.
- Make a 2-inch hole in the center of the container and carefully plant the seedling.
- Place the container in a location that receives at least 6 hours of sunlight daily.
- Provide steady and frequent watering for healthy growth.
- The ideal temperature to grow cabbage in the container is 59-69.8°F.
- Place the container in a location that receives at least 6 hours of sunlight.
- It takes 60-105 days for cabbage heads to mature fully. (based on its variety).
- Harvest when the heads are firm and reach 1-3 pounds.
How to Transplant Cabbage Seedlings?
Transplanting seedlings requires care to ensure that young plants establish well in their new place.
Follow below transplanting steps:
- Transplant seedlings when the plants reach about 3-4 inches in height.
- Harden off seedlings before transplanting them into the ground
- Get your soil ready by mixing in nutrient-rich compost
- Dig a hole a bit deeper than seed trays for proper rooting. Moisten the soil where your seedlings are in
- Gently squeeze trays to release seedlings from tray spaces
- Bury seedlings into the holes you dug, place soil around them, and gently pack them
- Keep seedlings moist during their growing stage
When to Plant Cabbage?
- For summer harvest, you can start seeds indoors
- Sow cabbage seeds about 6-8 weeks before the last spring frost date
- For a fall harvest, directly sow seeds outdoors in mid-to-late summer
- If your area is not hot and dry, hold off planting till late summer
- Ensure young plants don’t dry out in the summer sun’s heat
How to Plant Cabbage?
To plant cabbage, follow below-mentioned steps:
- Sow cabbage seeds about ½-¼ inch deep in the soil
- Before you plant the seedlings outdoors in the garden, harden off the plants over the course of a week
- Transplant seedlings outdoors on a cloudy noon about 2-3 weeks before the last spring frost date
- Plant them about 12-24 inches apart in rows, depending on the size of the desired head
Cabbage Growing Stages
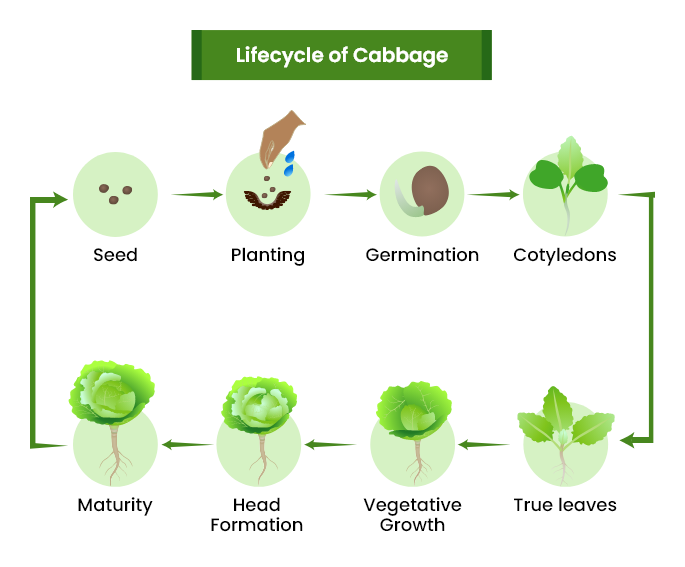
1. Germination
Sow seeds in a well-prepared tray or seedbed in early spring, around 4-5 weeks before the last frost date. Ensure the soil is well-draining and has a good balance of nutrients. Maintain soil temperature of 70°F for optimal seed germination.
Plant seeds about 6mm deep and cover them with soil or compost. Water them lightly. Keep the seedbed or trays moist. Emerging seedlings should receive adequate sunlight about 16 hours a day at a temperature of 60-80°F.
2. Seedlings
Transfer young cabbage plants from seedbeds to a permanent location like a garden bed or container. Transplant cabbage seedlings when they have 4-6 true leaves and when the weather is mild and there is no frost threat.
Select a location that offers afternoon shade and protects against strong winds. Mix compost or well-rotted manure into the soil. Once transplanted, seedlings require consistent moisture (6 hours), good drainage, and protection from pests.
3. Vegetative Growth
The cabbage plant produces several leaves and undergoes significant growth in width and height. It establishes its root system, which absorbs water and nutrients required for proper growth.
This stage lasts about 60 to 90 days, after which the plant has reached maturity and is ready for harvesting. Harvesting before the reproductive stage ensures the best quality and flavor.
4. Flowering
A long, thin, flowering stem emerges from the center of the plant. The cabbage plant diverts its resources and energy from leaf growth to the formation of flowers. The stem grows upwards, up to 1 meter in some cultivars, and produces small, yellow flowers at the stem’s tip.
The flowers are self-fertile and contain both male and female reproductive structures. Once the flowers are pollinated, they develop into small, round seed pods which contain the plant’s offspring.
How to Harvest Cabbage?
Harvesting should be done before the rainfall to avoid damage to the cabbage heads. The best way to harvest cabbage is by cutting it. Cut it at the lowest point and leave loose outer leaves attached to the stalk.
It allows for a later harvest of cabbage sprouts, which grow on the stem after removing the cabbage head. Reason? Mature heads will be split by excessive rainfall or overwatering, making them inedible.
- Headed cabbage should be cut from the plant’s base using a sharp knife when it feels solid and firm.
- Harvest cabbage when the head is about the size of a softball, 5 inches or more across. Squeeze it to test its firmness.
- You can also harvest cabbage by pulling up the plant roots and all.
- If the cabbage head starts cracking before harvest time, give the head a 180° twist at ground level.
- The twist will break off some roots and slow the head’s growth.
- After harvesting, remove the stem and root system from the soil to prevent disease.
How to Store Cabbage?
Store the cabbage head properly to keep it fresh, delicious, and crunchy for a long time. You can prolong the shelf life of this leafy vegetable by weeks and even months when stored properly.
Follow these steps to store cabbage for a long time:
- Wash it only when you are ready to use it.
- Place it in the crisper drawer section of the refrigerator.
- Store it in a large plastic storage bag to retain its natural moisture.
- If you have a partial head of cabbage, store it in an airtight container to lock in its moisture
Best Cabbage Varieties
Each variety serves a different purpose and people use it in different recipes.
1. Red Acre Cabbage
This variety has a bright purple-red cabbage head. This fantastic variety can be grown in the garden and proves a healthy eating option. Compared with other varieties, it has a sweet flavor so you can use it in raw salads or coleslaw recipes. Ensure you offer plenty of water and adequate drainage to this cabbage variety.
2. January King
This heirloom cabbage variety is one of the cold, hardy plants that can be grown in your garden. It features massive purple and green leaves, which are sweet and tender. Its head weighs about 3-5 pounds, which takes approximately 150-200 days to mature fully.
It is used for storage and gardening in winter. Plant this variety in full sunlight and space them at least 18-24 inches apart.
3. Parel Cabbage
It is another early-season cabbage ready to harvest in 40-45 days. It takes about 6-7 weeks from start to finish to grow fully as cabbage heads.
Its outer leaves have a bluish-green color, which is juicy and sweeter than other cabbage types. You can use it in different recipes, raw salads, coleslaws, pickles, or roast them.
Common Pests and Diseases Problems with Cabbage
Cabbage is susceptible to different pests and diseases, affecting its growth and yield. Some pests affecting cabbage growth are cabbage worms, aphids, root maggots, caterpillars, armyworms, and cabbage loopers.
Diseases affecting the cabbage yield are clubroot, black rot, bottom rot, mosaic virus, white rust, blackleg, ring spot, Alternia leaf spot, bacterial soft rot, powdery mildew, and downy mildew.
Companion Plants for Cabbage

Companion plants help maximize use of space, the proper use of soil nutrients, and pest management. It reduces the need for chemical pesticides and promotes healthy and productive crops.
These plants attract beneficial insects and repel unwanted pests, helping the crop flourish further. Parsley, potatoes, buckwheat, celery, garlic, peppermint, oregano, spearmint all make great companion plants for cabbage crop.





